Microsoft warns of a growing number of nation-states and criminals increasingly exploiting publicly disclosed zero-day vulnerabilities to infiltrate target environments.
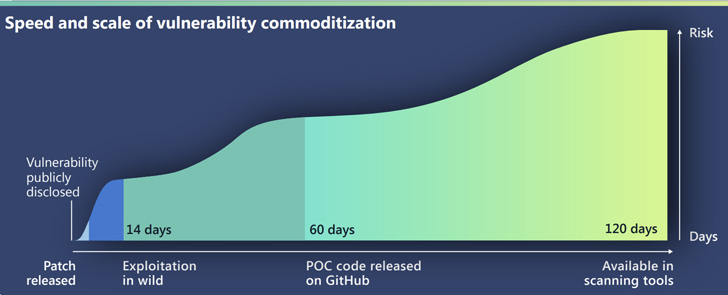
114-page tech giant Digital defense reportstated that it “observed a reduction in the time between the announcement of a vulnerability and its commoditization,” making it imperative for organizations to patch such exploits in a timely manner.
This is also consistent with an advisory issued by the US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) in April 2022. In this advisory, we discovered that malicious actors are “aggressively” targeting newly disclosed software bugs to a wide range of targets around the world.
Zero-day attacks, while initially limited in scope, have been quickly adopted by other threat actors, noting that it only takes an average of 14 days from disclosure of the vulnerability to the availability of an exploit in the wild, according to Microsoft. said to tend to be Probe events are fired indiscriminately before a patch is installed.
He also accused Chinese government-backed groups of being “particularly adept” at finding and developing zero-day exploits.
This is exacerbated by the fact that China’s Cyberspace Administration (CAC) has enacted new vulnerability reporting rules in September 2021. The regulation requires reporting security flaws to the government before sharing them with product developers.
Redmond further said the law would allow government-backed elements to stockpile and weaponize reported bugs, with the aim of furthering China’s economic and military interests. He said the use of zero-days for espionage could increase.
Some of the vulnerabilities initially exploited by Chinese actors, before being discovered by other adversary groups, include:
- CVE-2021-35211 (CVSS Score: 10.0) – A remote code execution flaw in SolarWinds Serv-U Managed File Transfer Server and Serv-U Secure FTP software exploited by DEV-0322.
- CVE-2021-40539 (CVSS Score: 9.8) – Zoho ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus authentication bypass flaw exploited by DEV-0322 (TiltedTemple).
- CVE-2021-44077 (CVSS score: 9.8) – Unauthenticated remote code execution flaw in Zoho ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus exploited by DEV-0322 (TiltedTemple).
- CVE-2021-42321 (CVSS score: 8.8) – A remote code execution flaw in Microsoft Exchange Server that was exploited three days after being disclosed during the Tianfu Cup hacking contest on October 16-17, 2021.
- CVE-2022-26134 (CVSS score: 9.8) – A flaw in Atlassian Confluence’s Object-Graph Navigation Language (OGNL) injection that, just days before the flaw’s disclosure on June 2, a Chinese-linked attacker made an unnamed U.S. You may have abused it against an entity.
The findings also come nearly a month after CISA published its list. top vulnerabilities It has been weaponized by China-based attackers since 2020 to steal intellectual property and develop access to sensitive networks.
“Zero-day vulnerabilities are a particularly effective vehicle for early exploitation, and once exposed, vulnerabilities can be rapidly reused by other nation states and criminals,” the company said. .



