Towards the end of 2022, the most worrying threats of this turbulent year, in terms of test numbers, are what motivate cybersecurity teams to check how vulnerable they are to specific threats. Get a threat-based perspective. These are the most tested threats to validate resilience. Cymulate Security Posture Management Platform From 1 January to 1 December 2022.
Manjuzaka
Publication date: August 2022
Reminiscent of the Cobalt Strike and Sliver frameworks (both commercially created and designed for red teams, but abused and exploited by threat actors), this new attack framework is designed to It has the potential to be widely used. Written in Rust and Golang, the user interface is in Simplified Chinese (see workflow diagram below), and the software is of Chinese origin.
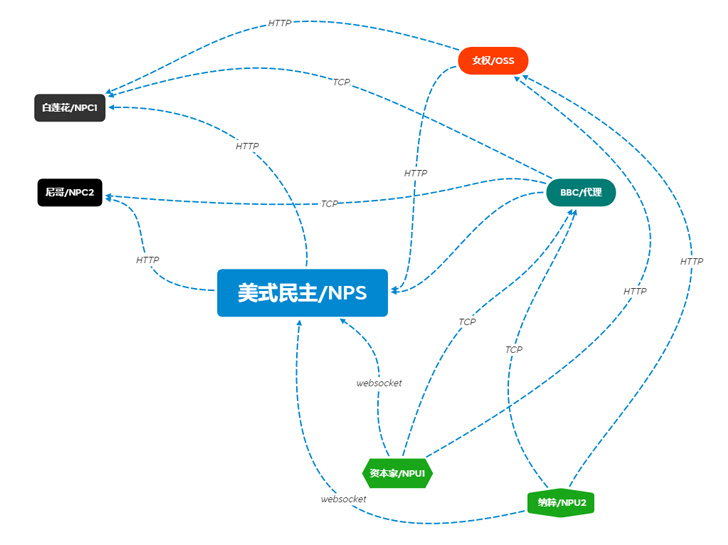
Manjusaka carries Windows and Linux implants in Rust, makes off-the-shelf C2 servers freely available, and allows custom implants to be created.
Geopolitical background
Manjusaka was designed from the ground up for criminals and will be distributed for free in 2023, including Cobalt Strike, Sliver, Ninja, Bruce Ratel C4 and more.
At the time of writing, there was no indication that Manjuzaka’s creator had state backing, but as clearly demonstrated below, China is not resting this year.
PowerLess backdoor
Publication date: February 2022
Powerless Backdoor was this year’s most popular Iran-related threat designed to evade PowerShell detection. Its capabilities include downloading browser information stealers and keyloggers, encrypting and decrypting data, executing arbitrary commands, and activating kill processes.
Geopolitical background
The number of imminent threats originating from Iran jumped from 8 to 17, more than double the number for a similar period in 2021. However, it has slowed significantly since the US Treasury Department’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) on September 14th. Sanctions against Iranian cybercriminalswhich has since led to a single attack attributed to Iran.
Current political tensions within Iran will undoubtedly affect the frequency of attacks in 2023, but at this stage it is difficult to assess whether attacks will increase or decrease.
APT 41 Targets US State Governments
Publication date: March 2022
APT41 was already noted to be very active in 2021, but the Chinese government-backed threat group showed no signs of slowing down in 2022. An investigation into APT41 activity has uncovered evidence of a deliberate campaign targeting US state governments.
APT 41 uses reconnaissance tools such as Acunetix, Nmap, SQLmap, OneForAll, subdomain3, subDomainsBrute, and Sublist3r. It also launches various types of attacks, including phishing, watering holes, and supply chain attacks, exploiting various vulnerabilities to compromise victims first. Recently, the public tool SQLmap has been seen to be used as the first attack vector to perform SQL injections on websites.
This November, a new subgroup, Earth Longhi, joined the already long list of names associated with APT 41 (ARIUM, Winnti, LEAD, WICKED SPIDER, WICKED PANDA, Blackfly, Suckfly, Winnti Umbrella, Double Dragon). rice field. Earth Longhi was spotted targeting multiple sectors in Taiwan, China, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, Pakistan, and Ukraine.
Geopolitical background
according to Microsoft Digital Defense Report 2022, “Many of the attacks from China are powered by the ability to find and compile ‘zero-day vulnerabilities’. This is an unpatched software-specific vulnerability that the security community has never known before. The collection of these vulnerabilities by China appears to have increased since then. New law requiring Chinese companies to report vulnerabilities they discover to the government before sharing them with others. ”
LoLzarus Phishing Attack Against DoD Industry
Publication date: February 2022
Called LolZarus, the phishing campaign attempted to lure job seekers in the US defense sector. The campaign was first identified by Qualys Threat Research and attributed to the North Korean actor Lazarus (AKA Dark Seoul, Labyrinth Chollima, Stardust Chollima, BlueNoroff, and APT 38). The group, affiliated with North Korea’s Reconnaissance General Bureau, is politically and financially motivated, most notably for his high-profile attack on Sondy in 2016 and his WannaCry ransomware attack in 2017. was well known.
The LolZarus phishing campaign relied on at least two malicious attacks. Documentation, Lockheed_Martin_JobOpportunities.docx When Salary_Lockheed_Martin_job_opportunities_confidential.doc, It relied on the ActiveX Frame1_Layout to automate the execution of the attack, renaming the API it used by abusing macros with aliases. The macro then loaded the WMVCORE.DLL Windows Media dll file to help deliver the second stage shellcode payload for control hijacking and connection to the Command & Control server.
Geopolitical background
Two other notorious North Korean attacks reported by CISA this year include the use of Maui ransomware and cryptocurrency theft activity. His BlueNoroff, a subgroup of Lazarus, seems to have branched out from the cryptocurrency specialization this year and is also targeting his crypto-connected SWIFT servers and banks. Cymulate has linked seven imminent threats to Lazarus since January 1, 2022.
Industry 2
Publication date: April 2022
Ukraine’s alert posture has proven effective in thwarting attempted cyber-physical attacks targeting high-voltage substations due to its conflict with Russia. The attack, dubbed Industroyer2 to commemorate the 2016 Industroyer cyberattack, apparently targeted a Ukrainian power plant and cut off power in parts of Kyiv for about an hour.
Industroyer2’s level of customized targeting included a statically specified set of executables with parameters specific to a particular substation.
Geopolitical background
Ukraine’s cyber resilience to protect critical facilities is unfortunately powerless against dynamic attacks, and Russia now resorts to more traditional military means to destroy power plants and other civilian facilities. According to Enisaa side effect of the Ukrainian-Russian conflict is the resurgence of cyber threats to governments, businesses, and critical sectors such as energy, transport, banking, and digital infrastructure.
In conclusion, out of the five most concerning threats this year, four are directly related to state-sponsored actors, while the actor behind the fifth is unknown. For cybersecurity teams.
Because state-sponsored attackers typically have access to cyber resources that most enterprises cannot reach, preemptive defense against complex attacks focused on security verification and contextually identifying and closing security gaps. We need to focus on ongoing processes.
Note: This article was written and contributed by Cymulate Cyber Evangelist David Klein.


