Government agencies and large organizations are being targeted by unknown attackers who exploit security flaws in Fortinet FortiOS software resulting in data loss, OS and file corruption.
“The complexity of the exploit suggests it is by sophisticated actors and highly targeted against government or government-affiliated targets,” said Fortinet researchers Guillaume Lovet and Alex Kong. I’m here. Said On last week’s recommendations.
The zero-day defect in question is CVE-2022-41328 (CVSS score: 6.5), a moderate security path traversal bug in FortiOS that could lead to the execution of arbitrary code.
Improper Restriction of Pathnames to Restricted Directories Vulnerability (“Path Traversal”) [CWE-22] FortiOS may allow a privileged attacker to read and write arbitrary files via crafted CLI commands,” the company notes.
This shortcoming affects FortiOS versions 6.0, 6.2, 6.4.0 – 6.4.11, 7.0.0 – 7.0.9, and 7.2.0 – 7.2.3. The fix is available for versions 6.4.12, 7.0.10, and 7.2.4 respectively.
This disclosure addresses 15 security flaws, including CVE-2022-41328 and a critical heap-based buffer underflow issue (CVE-2023-25610, CVSS score: 9.3) affecting FortiOS and FortiProxy. This was a few days after we released a patch to address it.
According to the Sunnyvale-based company, multiple FortiGate devices owned by an unnamed customer suffered a “sudden system outage followed by boot failure,” indicating an integrity violation.
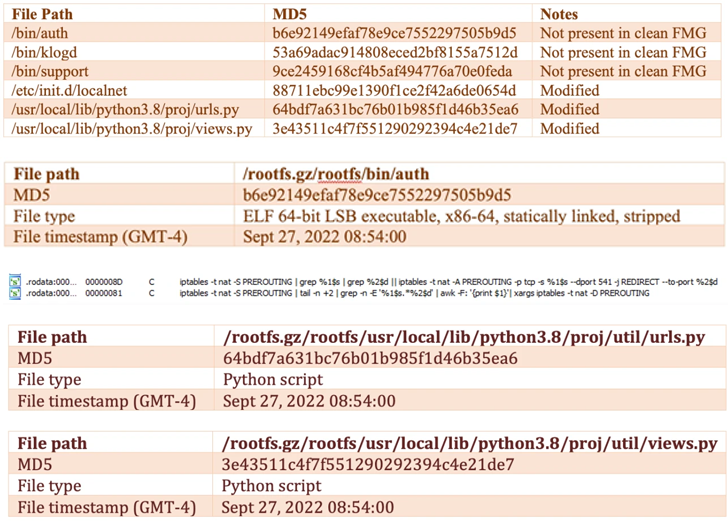
Further analysis of this incident reveals that the attacker modified the device’s firmware image to include a new payload (“/bin/fgfm”) so that it is always launched before the boot process begins. became.
/bin/fgfm malware is designed to establish connections with remote servers to download files, exfiltrate data from compromised hosts, and allow remote shell access.
Additional modifications introduced to the firmware allegedly gave the attackers persistent access and control, and even allowed them to disable firmware verification at boot time.
Discover the hidden dangers of third-party SaaS apps
Are you aware of the risks associated with third-party app access to your company’s SaaS apps? Join our webinar to learn about the types of permissions granted and how to minimize the risks.
Fortinet said the attack was highly targeted and had evidence pointing to a government or government-affiliated entity.
Given the complexity of the exploit, we believe the attackers had a “deep understanding of FortiOS and its underlying hardware” and advanced capabilities to reverse engineer various aspects of the FortiOS operating system. .
Whether the threat actor is connected to another set of intrusions that were observed to weaponize the FortiOS SSL-VPN flaw (CVE-2022-42475) and deploy Linux implants in January of this year remains to be seen soon. don’t understand.


