Cybersecurity researchers have discovered an ongoing phishing campaign that utilizes a unique attack chain to deliver XWorm malware to targeted systems.
We track activity clusters under the name Securonix. Meme #4-chanSome of the attacks were primarily aimed at manufacturing companies and medical clinics located in Germany, according to the company.
“The attack campaign utilizes rather unusual meme-laden PowerShell code, which is then infected with a highly obfuscated XWorm payload,” said security researchers Den Iuzvyk, Tim Peck and Oleg Kolesnikov. said. Said In a new analysis shared with HackerNews.
The basis of the report is Recent discoveries A report from Elastic Security Labs uncovered the lure of reservation-themed threat actors tricking victims into opening malicious documents capable of delivering XWorm and Agent Tesla payloads.
Instead of using macros, this attack is a phishing distributing decoy Microsoft Word document that drops an obfuscated PowerShell script, weaponized with the Follina vulnerability (CVE-2022-30190, CVSS score: 7.8) Start with an attack.
From there, the attacker abuses a PowerShell script to bypass the antimalware scanning interface (AMSI), disable Microsoft Defender, establish persistence, and finally launch a .NET binary containing XWorm.
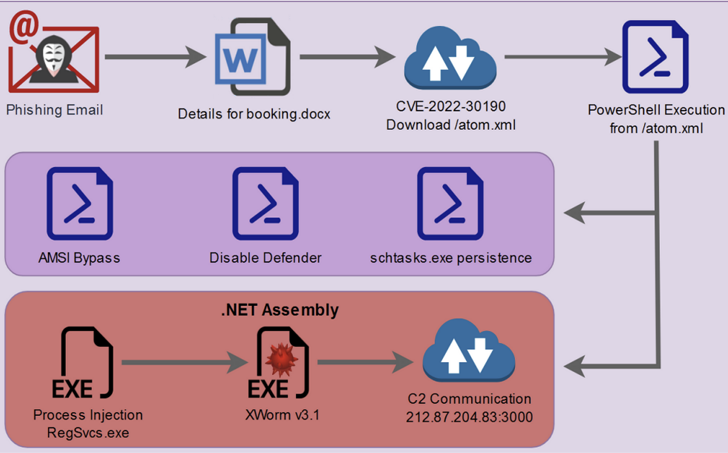
Interestingly, one of the variables in the PowerShell script is named “$CHOTAbheem”, which is likely a reference to: Chota Beaman Indian animated comedy-adventure television series.
The researchers told HackerNews, “A quick look suggests that the individual or group involved in the attack may have a Middle Eastern or Indian background, but final attribution has yet to be confirmed. ‘ and pointed out that such keywords were included. It can also be used as a cover.
The X-worm is commodity malware It is advertised for sale on underground forums and comes with a wide range of features that allow it to siphon sensitive information from infected hosts.
Learn how to stop ransomware with real-time protection
Join our webinar to learn how to stop ransomware attacks using real-time MFA and service account protection.
This malware is also a Swiss Army knife in that it can perform clipper, DDoS and ransomware operations, spread via USB and drop additional malware.
The exact origin of the threat actor is currently unknown, but Securonics said the attack technique contains artifacts similar to TA558, which has been observed to hit hospitality industries in the past.
“Since Microsoft made the decision to disable macros by default, Microsoft Office documents are rarely used in phishing emails, but today we have seen cases of malicious document files, especially VBscript execution, in this case. We still see evidence that it’s important to be vigilant, macro,” the researchers said.



