Two critical flaw chains were revealed in Alibaba Cloud’s ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL and AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL. This could be abused to break tenant isolation protections and gain access to sensitive data of other customers.
“This vulnerability allows unauthorized access to the PostgreSQL databases of Alibaba Cloud customers, allowing them to perform supply chain attacks against both Alibaba database services, potentially causing an RCE on the Alibaba database services. ,” said Wiz, a cloud security firm. Said In a new report shared with The Hacker News.
of problem,dubbing broken sesame seeds, was reported to Alibaba Cloud in December 2022 after mitigation measures were deployed by the company on April 12, 2023. There is no evidence to suggest that the vulnerability has been exploited in the wild.
In a nutshell, the vulnerabilities (the AnalyticDB privilege escalation flaw and the ApsaraDB RDS remote code execution bug) allow privileges to elevate to the root inside the container, escape to the underlying Kubernetes node, and finally to the API. It is now possible to obtain unauthorized access to server.
An attacker could leverage this feature to retrieve credentials associated with a container registry from an API server and push malicious images to control customer databases belonging to other tenants on shared nodes. there is.
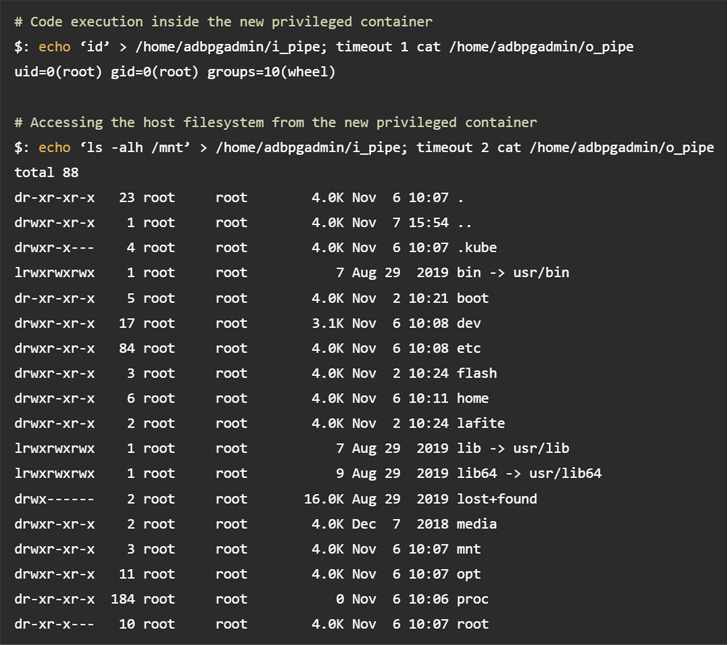
According to Wiz researchers Ronen Shustin and Shir Tamari, “The credentials used to pull the images were not properly scoped and allowed push permissions, creating a basis for supply chain attacks. I was working on it,” he said.
This is not the first time PostgreSQL vulnerabilities have been identified in cloud services. Last year Wiz found a similar issue with his Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server (ExtraReplica) and his IBM Cloud Databases for PostgreSQL (Hell’s Keychain).
Defending with Deception: Driving Zero Trust Security
See how Deception can detect advanced threats, stop lateral movement, and strengthen your Zero Trust strategy. Join us for an insightful webinar!
The findings are presented as Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 within. Cloud threat reportrevealed that “threat actors are adept at exploiting common everyday problems in the cloud.”
“76% of organizations do not have MFA in place [multi-factor authentication] For console users, 58% of organizations do not enforce MFA for root/admin users,” said the cybersecurity firm.



 Discovering the power of self-awareness
Discovering the power of self-awareness  #shorts #thinkbig
#shorts #thinkbig Self Awareness
Self Awareness November 17's Top Cyber News NOW! –...
November 17's Top Cyber News NOW! –... Happiness : Just Be
Happiness : Just Be 